
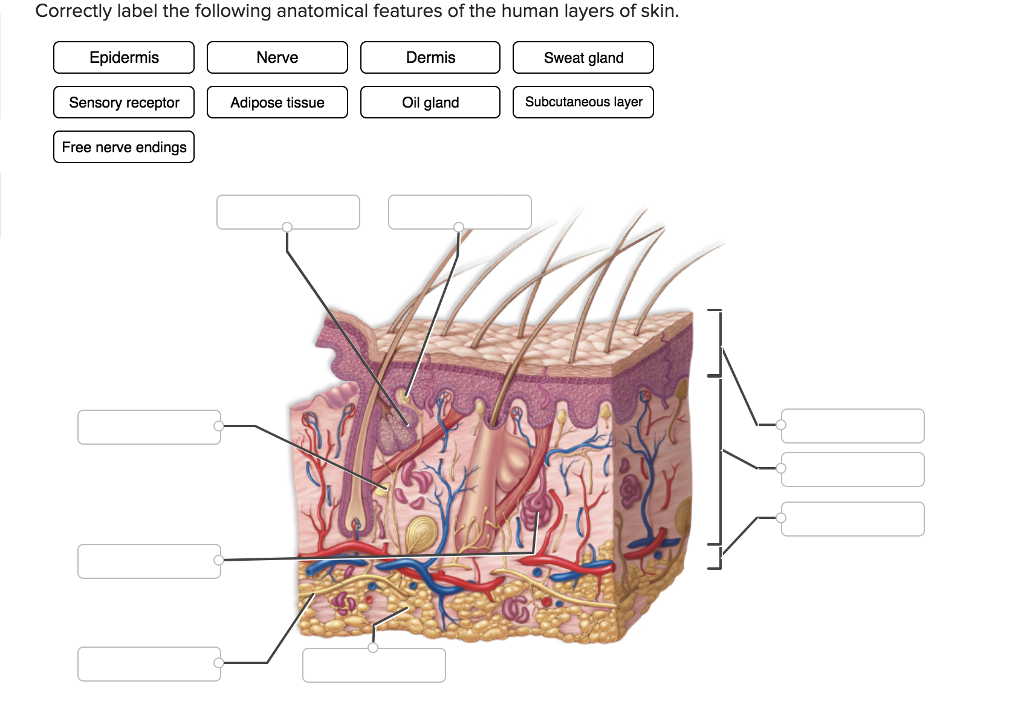
#FUNCTION OF FREE NERVE ENDINGS IN SKIN SKIN#
Tactile discs (of Merkel): They are expanded disc-like nerve endings in the germinative epidermal layer of hairless skin ( Fig.4.1 ): It is a network of dendritic branches that surrounds the outer root sheath of hair follicles and is stimulated by light touch causing movement of hair. Peritrichial or root hair plexus ( Fig.4.1 Sensory nerve endings (receptors) in skin. Most of these endings carry pain sensations ( pain fibres), but they are also sensitive to temperature, touch, pressure and tickle sensations.įIG. The terminal endings are devoid of a myelin sheath and there are no Schwann cells covering their tips. The afferent fibres from free nerve endings are either myelinated or non-myelinated. 4.1 ): They are widely distributed in the body tissues such as skin, cornea, periosteum, dental pulp, etc. Here the sensory nerve endings do not show any particular specialization of structure and are directly applied to the tissue cells or may lie freely in the extracellular spaces. Structurally the receptors are classified into two types: non-encapsulated and encapsulated. Osmoreceptors: They respond to changes in the osmotic pressure.Photoreceptors: They are stimulated by light, e.g.Damage to tissue is perceived as pain, discomfort or irritation. Nocireceptors: These respond to any stimuli that bring about damage to the tissue.Thermoreceptors: They respond to alternation in temperature, e.g.Chemoreceptors: They are stimulated by chemical influences.Mechanoreceptors: They are stimulated by mechanical deformation.On the basis of the manner in which they are stimulated Interoceptors: They provide information from viscera and blood vessels.Proprioceptors: They provide information about state of contraction of muscles and of joint movement and position.These are superficially located, such as in skin, and are also called cutaneous receptors. Exteroceptors: They provide information of touch, pain, temperature and pressure.On the basis of the kind of information they provide

The receptors can be classified broadly into: Thus, receptors are sensory nerve endings specialized for reception of stimuli and transmitting them in the form of nerve impulses. The receptors thus act as transducers, * converting mechanical and other stimuli into electrical impulses. The receptor receives stimulus and converts it into a nerve impulse. The knowledge of structure and function of sensory and motor nerve endings responsible for sensory input and motor output is essential while performing these tests.Īn individual receives information from outside and from within the body by special sensory nerve endings called receptors. Whenever a clinician performs a neurological examination in a patient, he/she tests for normal function of the sensory input and motor output so that he/she may find out any sensory or motor deficit if it is there.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
